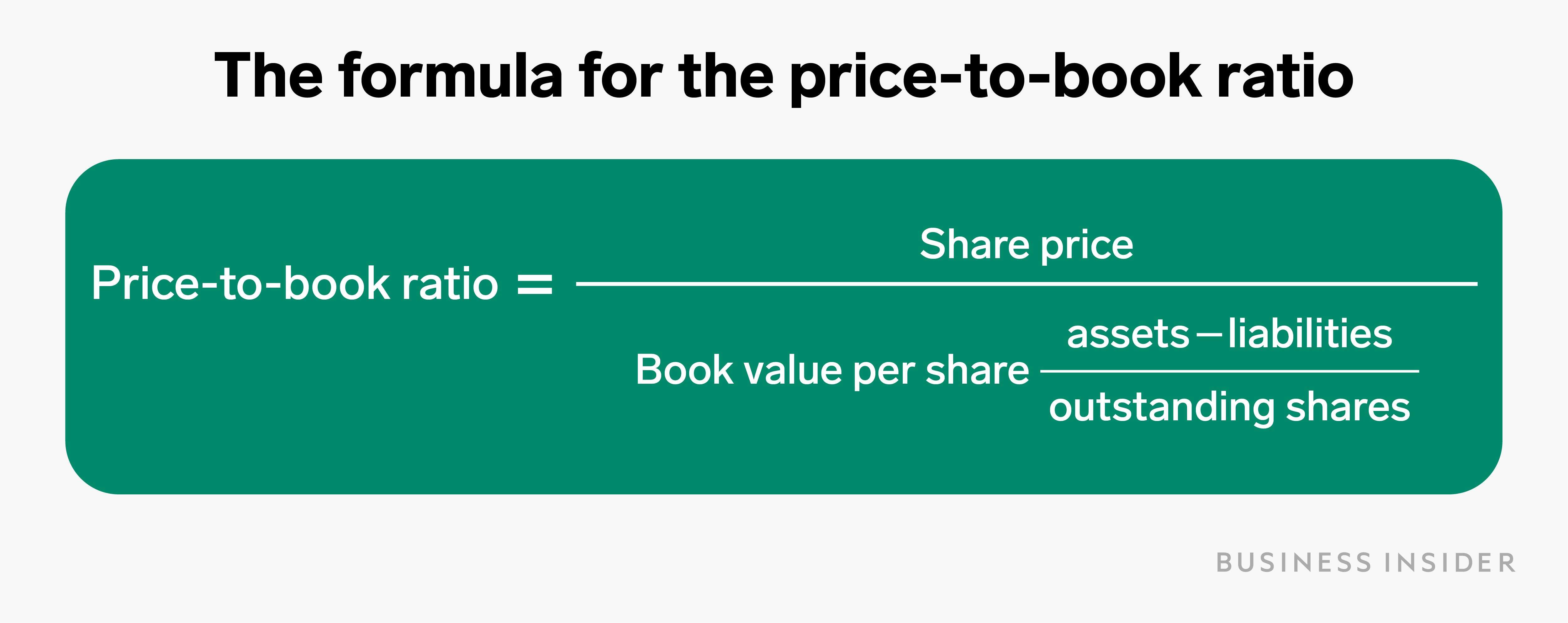
Sandra Habiger is a Chartered Professional Accountant with a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington. Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors. She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business. There are other factors that you need to take into consideration before making an investment. However, book value per share can be a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments.
How does BVPS differ from market value per share?
Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share. Book value refers to a firm’s net asset value (NAV) or its total assets minus its total liabilities. Assume that XYZ Manufacturing has a common equity balance of $10 million and 1 million shares of common stock are outstanding. This means that the BVPS is ($10 million / 1 million shares), or $10 per share. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases.
Formula to Calculate Book Value of a Company
It’s also a useful measure to compare a company with a lot of goodwill on the balance sheet to one without goodwill. In the food chain of corporate security investors, equity investors do not have the first crack at operating profits. Common shareholders get whatever is left over after the corporation pays its creditors, preferred shareholders and the tax man. But in the world of investing, being last in line can often be the best place to be, and the common shareholder’s lot can be the biggest piece of the profit pie. In closing, it’s easy to see why the book value per share is such an important metric. It’s a simple way to compare the value of a company’s net assets to the number of shares that are outstanding.
The Difference Between Book Value per Share and Net Asset Value (NAV)
- Intangible assets have value, just not in the same way that tangible assets do; you cannot easily liquidate them.
- She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond.
- To calculate the book value per share, you must first calculate the book value, then divide by the number of common shares.
- Comparing BVPS to the market price of a stock is known as the market-to-book ratio, or the price-to-book ratio.
Remember, even if a company has a high book value per share, there’s no guarantee that it will be a successful investment. The book value per share is just one metric that you should look at when considering an investment. It’s important to remember that the book value per share is not the only metric that you should consider when making an investment decision. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock is trading below or above its intrinsic value. With those three assumptions, we can calculate the book value of equity as $1.6bn.
Methods to Increase the Book Value Per Share
By analyzing BVPS, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health and intrinsic value, aiding in the assessment of whether a stock is over or undervalued. We’ll assume the trading price in Year 0 was $20.00, and in Year 2, the market share price increases to $26.00, which is a 30.0% year-over-year increase. Price-to-book (P/B) ratio as a valuation multiple is useful when comparing xero community similar companies within the same industry that follow a uniform accounting method for asset valuation. It can offer a view of how the market values a particular company’s stock and whether that value is comparable to the BVPS. There is a difference between outstanding and issued shares, but some companies might refer to outstanding common shares as issued shares in their reports.
What Book Value Means to Investors
If it’s obvious that a company is trading for less than its book value, you have to ask yourself why other investors haven’t noticed and pushed the price back to book value or even higher. The P/B ratio is an easy calculation, and it’s published in the stock summaries on any major stock research website. Hence, the investor needs to have looked upon both the book value or the book price of the company as well as the market price of the stock and then decide on the company’s worthiness. The 2nd part divides the shareholders’ common equity, which is available to the equity shareholders by the unprecedented number of common equity shares. The book value per share of a company is the total value of the company’s net assets divided by the number of shares that are outstanding.
For example, if the BVPS is greater than the MVPS, the company’s stock market may be undervaluing a company’s stock. Now, let’s say that XYZ Company has total equity of $500,000 and 2,000,000 shares outstanding. In this case, each share of stock would be worth $0.50 if the company got liquidated. Book Value Per Share is calculated by dividing the total common equity by the number of outstanding shares.

BVPS is more relevant for asset-heavy companies, such as manufacturing firms, where physical assets constitute a significant portion of the balance sheet. BVPS is typically calculated quarterly or annually, coinciding with the company’s financial reporting periods. In other words, investors understand the company’s recent performance is underwhelming, but the potential for a long-term turnaround and the rock-bottom price can create a compelling margin of safety. The figure of 1.25 indicates that the market has priced shares at a premium to the book value of a share. If the market price for a share is higher than the BVPS, then the stock may be seen as overvalued.
In this case, the shares outstanding number is stated at 3.36 billion, so our BVPS number is $71.3 billion divided by 3.36 billion, which equals $21.22. Each share of common stock has a book value—or residual claim value—of $21.22. At the time Walmart’s 10-K for 2012 came out, the stock was trading in the $61 range, so the P/BVPS multiple at that time was around 2.9 times.
BVPS is the book value of the company divided by the corporation’s issued and outstanding common shares. Book value per share is the portion of a company’s equity that’s attributed to each share of common stock if the company gets liquidated. It’s a measure of what shareholders would theoretically get if they sold all of the assets of the company and paid off all of its liabilities. To calculate the book value per share, you must first calculate the book value, then divide by the number of common shares. Also, since you’re working with common shares, you must subtract the preferred shareholder equity from the total equity. There are many methods that investors can use to evaluate the value of a company.
The book value of a company is based on the amount of money that shareholders would get if liabilities were paid off and assets were liquidated. The market value of a company is based on the current stock market price and how many shares are outstanding. Book Value per Share (BVPS) is the ratio of a company’s equity available to common shareholders to the number of outstanding company shares. This ratio calculates the minimum value of a company’s equity and determines a firm’s book value, or Net Asset Value (NAV), on a per-share basis. In other words, it defines the accounting value (i.e. book value) of a share of a company’s publicly-traded stock. For example, Walmart’s January 31, 2012 balance sheet indicates that shareholders’ equity has a value of $71.3 billion.

No comment